The Northern Lights (also known as aurora borealis) is a bucket-list phenomenon that lights up the skies as the sun’s particles hit the Earth. But, as the name implies, they can only be seen in northern parts of the world. But, just how far north can they be seen?
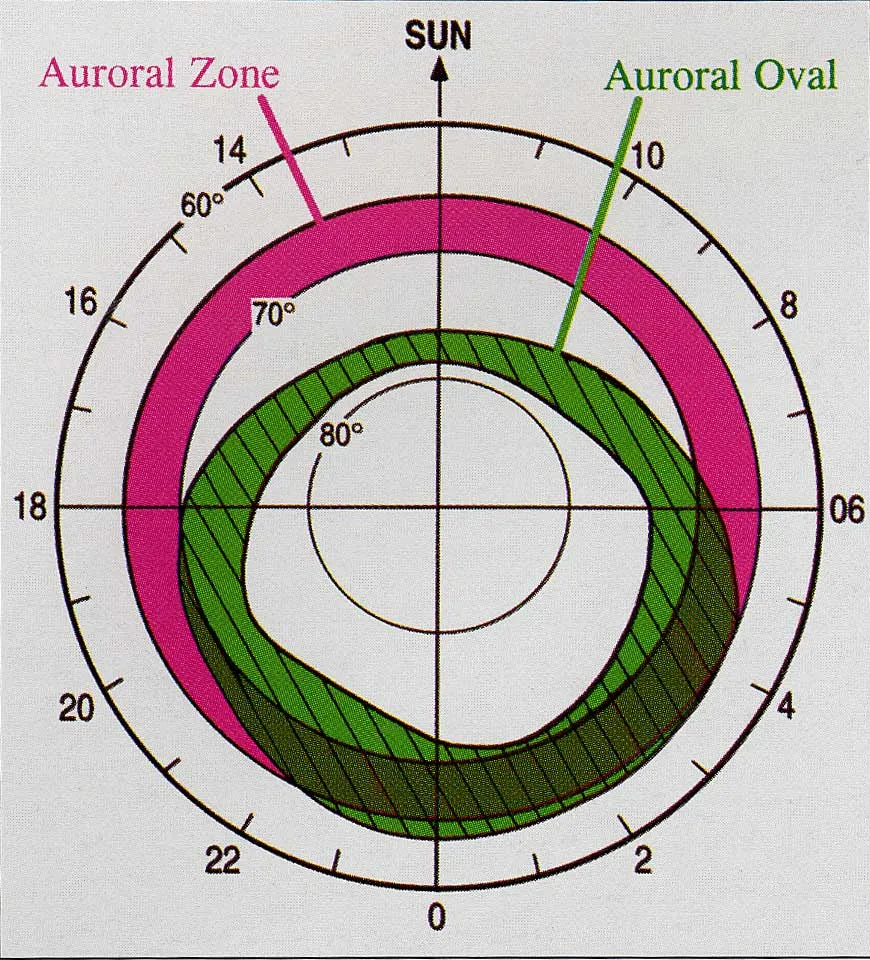
The best place to see the Northern Lights changes depending upon how the sun’s particles are hitting Earth. Typically, you are most like to see the aurora between 65° and 70° latitude, an area known as the Auroral Zone. This covers parts of Alaska, Canada, Russia, Greenland, Finland, Norway, Sweden, and Iceland.
Keep reading to find out more about the Auroral Zone and how it is different from the Auroral Oval.
How Far North are the Northern Lights?
The latitude (how far north) at which you can see the Northern Lights changes all the time, although there are places where you are more likely to see them and places where you are less likely to see them.
To understand this, there are two things you need to know about the Auroral Zone and the Auroral Oval.
What is the Auroral Zone?
The northern lights are most commonly seen in the Auroral Zone, this is an imaginary zone around the world between 65° and 70° latitude. This is between 7,211km and 7,766km (4,480-4825 miles) above the equator.
The Auroral Zone is near the arctic circle and covers northern parts of Alaska, Canada, Russia, Finland, Norway, Sweden, and Iceland, as well as the middle of Greenland.
Being in the Auroral Zone does not guarantee that you’ll see the phenomenon, but it greatly increases your chances. The further away from the Auroral Zone you are, the lower your chances of seeing the Northern Lights on any given date1 (source: D. Underwood, The Northern Lights, 2004).
Although you can often see the Northern Lights at the North Pole, this is not the best place to see them as this is above the Auroral Zone.
What is the Auroral Oval?
Where the Northern Lights actually appear in the sky is called the Auroral Oval. This is not imaginary and can be mapped using special equipment. The Auroral Oval is usually about 4000km (2500 miles) across2 (source: D. Underwood, The Northern Lights, 2004).
Unlike the Auroral Zone which is fixed, the Auroral Oval changes all the time. When the sun projects more electronically charged particles at Earth, the oval is stretched and protrudes further south. The Auroral Oval rotates around the Auroral Zone as shown in this image.
In 1958, when solar activity peaked, the Auroral Oval stretched down as far as Mexico with the Northern Lights being seen by residents in Mexico City3 (source: The Aurora Zone).
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) provide a live 30-minute forecast of the Auroral Oval which indicates where you are most likely to see the Northern Lights right now.
There are also a southern Auroral Zone and Auroral Oval where you can see the Southern Lights.


![You are currently viewing How Far North are the Northern Lights? [Auroral Zone and Oval Explained]](https://polarguidebook.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Northern-Lights.jpg)